Ignored Safety Signals
Safety Signals by PRR as of March 31st 2021
If you have any literature references to add or come across any errors or inaccuracies, please do let me know in the comment section.
Summary
I am presenting retrospective safety signals based on proportional reporting ratios among spontaneous reports in this article, utilizing only reports that were processed by March 31st, 2021.
There are four important early signal clusters emerging from spontaneous reports:
Cardiac signals made up of arrythmias and concepts surrounding heart attacks
Cerebrovascular signals, both haemorrhagic and ischemic
With 4 affected nerves, non-vascular neurological signals are almost exclusively related to cranial nerve dysfunction
Reproductive system disorders centered around menstruation
Population-level data shows that proportions of decedents who had diagnoses for cerebrovascular disease, acute myocardial infarction or lung embolisms were either peaking in 2021 and 2022 or - in the case of acute myocardial infarction - diverging upwards from the previous downward trend.
While cardiac complications of COVID vaccination have been well-described in scientific literature, this is not the case for neuroinflammatory and hypercoagulative disorders. Except for Bell’s palsy cranial nerve dysfunction after COVID vaccination has received little attention from the scientific community.
Introduction
Some of you will be familiar with my safety signal website pervaers.com. It offers a nearly complete list of age-adjusted safety signals for all vaccine types by antigen based on “proportional reporting differences” to proportions among reference report cohorts, giving patients and clinicians an idea of how common certain vaccine adverse events are.
A more common way to identify safety signals are PRR s (proportional reporting ratios). PRRs are a popular method to identify unusual increases in certain medical concepts among spontaneous reports submitted to post-approval pharmacovigilance databases like VAERS.
As of today, there still is no complete listing of PRRs publically available - not anywhere I know of. I decided to go back to my U.S. VAERS signals and present the most important signals to you, starting with past signals for Pfizer from March 2021, using an old version of the database.
These signals are the ones that could have been identified very early on, before the damage was done.
As already mentioned I limited this analysis to Pfizer reports (excluding all SARS-CoV-2 infection reports). Depending on how well this article is received I might write one on early Moderna and Johnson signals as well.
We will also look at population-level data to see if any of the signals are reflected in mortality.
Methods
You can find a detailled explanation of how proportional reporting ratios are calculated in the help section of pervaers.com.
Safety signals
For each analysis, all reports are first split into 2 groups:
A study report cohort. In this case we will be using reports processed as of March 2021, submitted in response to adverse events occurring after administration of COVID vaccines by Pfizer
A control report cohort, containing all remaining reports that were submitted in response to adverse events occurring after administration of non-COVID vaccines
For the age-adjusted analysis, age adjustment of the two cohorts is performed (but we are just looking at crude signals today)
The occurrences of each medical concept in both cohorts are counted
The number of occurrences is then divided by the number of reports in that cohort, yielding “report proportions”
The ratio of report proportions between the two cohorts is the “proportional reporting ratio”. When a concept is significantly (p<0.1) overrepresented, a signal is generated
Population-level data
I join monthly (2015-2017) and weekly (2018-2022) data by converting each to pseudo-daily data. Think of this as data with monthly precision with a little extra granularity.
Proportions of one mortality type among another type are calculated
2015-2019 serves as reference timeframe for calculation of excess proportions, which are calculated by taking the difference between the expected and actual proportion.
Downloads
All Signals, 24 files in total:
by product (Pfizer, Moderna, Johnson, any COVID vaccine)
by snapshot time (March 2021, January 2023)
by method (crude, age-adjusted, pseudo-placebo reference)
I will only be presenting the strongest signals and the ones I consider most important, since there are just way too many overall to discuss them all in one article.
We will only be looking at crude signals. Age-adjusted ones and those utilizing pseudo-placebo reference cohorts can be found in the download package and are mostly in the same ballpark, but have wider confidence intervals due to the uncertainty introduced by age-adjustment.
Results
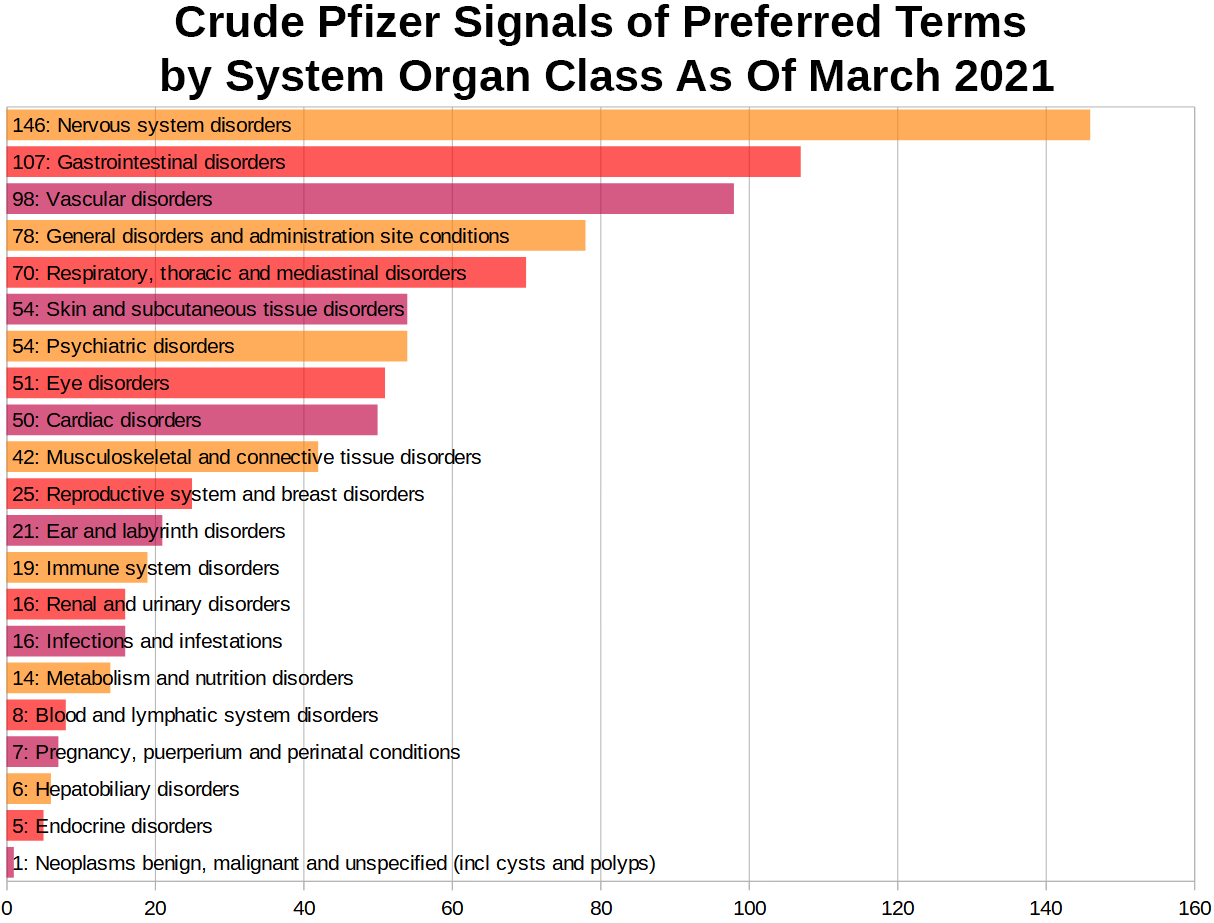
SOC stands for System Organ Class, the highest level of hierarchy in the MedDRA system. To give you an idea how early signals were distributed across these top-level categories, I will present a chart representing the number of lowest hierarchy levels signals - Preferred Terms - in each SOC.
PT Distribution across SOCs
There were 358 unique signals for Preferred Terms as of March 2021 among Pfizer reports. Some of these exist in multiple SOCs. For example, “taste disorder” is present in both nervos system and gastrointestinal disorders.
Keep in mind that these are very early signals. The distribution changed profoundly throughout the course of the vaccination campaign. Especially the number of cancer signals increased massively later on.
Now for a more detailled look at the Pfizer signals, I will group them into SOCs as long as there are enough important signals in a category.
PRRs by SOC
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA), also known as electromechanical dissociation, describes a state where electrical impulses are still being generated and conducted by the specialized cardiac muscle cells responsible for this, but the remaining cardiomyocytes are not responding to this with contractions - resulting in a heart that is not beating.
Coronary artery stenosis/obstruction occurs when the coronary arteries — the blood vessels supplying blood to the heart — narrow. This narrowing can restrict blood flow to the heart, causing oxygen deficiency accompanied by symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
With or without treatment, coronary arteries can become completely blocked, a condition called chronic total occlusion. Coronary artery stenosis ultimately leads to myocardial infarction.
Review of myocardial infarctions after modRNA vaccine administration
Acute myocardial infarction or heart attack is myocardial necrosis resulting from acute obstruction of a coronary artery. Symptoms include radiating chest pain from mild to unbearably painful, dyspnea, nausea and diaphoresis (excessive sweating without physical exertion).
Review of myocardial infarctions after modRNA vaccine administration
Cardiogenic shock is a life-threatening condition in which your heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet your body's needs. The condition is most often caused by a severe heart attack, but not everyone who has a heart attack experiences cardiogenic shock.
Review of myocardial infarctions after modRNA vaccine administration
A relatively common and often benign type of arrythmia that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. When it occurs, it is associated with an elevated pulse, that represents an unstable rythm which often degrades into (less benign) atrial fibrillation.
A short article on arrythmias occurring after COVID vaccination
This is just a heartbeat of over 100 beats per minute. The excitation begins in the sinus node - where it should begin - and spreads regularly. Just a high heart beat with a scary name.
A short article on arrythmias occurring after COVID vaccination
Palpitations are perceived abnormalities of the heartbeat characterized by awareness of cardiac muscle contractions in the chest, which is further characterized by hard, fast and/or irregular beating of the heart.
Palpitations are not always accompanied by actual arrythmias and arrythmias are not always accompanied by palpitations.
A short article on arrythmias occurring after COVID vaccination
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an abnormal heart rhythm (i.e. arrhythmia) characterized by rapid and irregular beating of the atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal beating, which become longer or continuous over time.
It can be a consequence of myocarditis and myocardial infarctions and can result in heart failure or stroke among other complications.
A short article on arrythmias occurring after COVID vaccination
Extrasystoles are another benign form of arrythmia corresponding to a premature contraction of one of the chambers of the heart. They typically have no long-term complications and do not require treatment.
Exertional dyspnea is dyspnea that presents with exercise and improves with rest.
Dyspnea is - like palpitations - a symptom and describes the perceived difficulty to breathe. It impacts millions of people and is often the main manifestation of respiratory, cardiac, neuromuscular, psychogenic or other illnesses.
Chest discomfort often accompanies respiratory and cardiac disorders, like myocardial infarctions, pulmonary embolisms, myopericardits or pneumonia.
Review of myocardial infarctions after modRNA vaccine administration, warning of chest discomfort
Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, is caused by reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV), the same virus that causes varicella (chickenpox).
Primary infection with VZV causes varicella. After a person has varicella, the virus remains latent in the dorsal root ganglia (nerve cells). VZV can reactivate later in a person’s life and cause herpes zoster, a painful maculopapular and then vesicular rash.
Review of post-vaccination Herpes Zoster reinfection articles
Painful lymph nodes usually occur as a result of vaccination or infection from bacteria or viruses. Less commonly, swollen lymph nodes are caused by cancer.
Dr. Edmonds of Penn Medicine explains “Lymph node swelling following the COVID-19 vaccine isn’t even technically an adverse response. It’s simply a response.”
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency.
Dr. Edmond of Penn Medicine approves of lymphadenopathy after COVID vaccination, because “It means you're responding. We just don't want to confuse it with a bad thing.”
Intermenstrual bleeding or metrorrhagia is just menstrual bleeding at unexpected points in time without any changes in the timing of periods.
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a disruptive set of emotional and physical symptoms that regularly occur in the one to two weeks before the start of each menstrual period. It is often accompanied by headaches, breast tenderness and bloating.
Polymenorrhoea occurs when menstrual cycles are shorter than usual (28 days), leading to more frequent periods.
While often described as contractions of the pelvic floor muscles occurring spontaneously, uterine spasms can also be a complication of giving birth. A look at individual reports could clear up how this signal is to be understood.
Penn Medicine tells us “Swelling after the COVID vaccine or booster can actually be considered good.”
Nipple pain / Breast discomfort
In most cases, sore nipples are caused by hormonal changes from pregnancy or menstruation, allergies or friction from clothing. In rare cases, it can be a sign of a serious disease like breast cancer.
An article on how COVID vaccination symptoms can mimic breast cancer
This can mean both lactation and discharge of other bodily fluids, the latter of which can represent signs of breast cancer.
An article on how COVID vaccination symptoms can mimic breast cancer
The central retinal vein is the most important vessel responsible for draining blood from the retina. RVO is a blockage of the central retinal vein usually manifests secondary to inherited or acquired vascular or metabolic disorders.
Retinal artery occlusion is usually caused by blood clots. The retinal artery supplies blood to the retina.
A case report about retinal artery occlusion occurring post COVID vaccination
Retinal migraines are a type of migraine that affect the eyes. They can cause temporary vision loss in the affected eye and other ocular symptoms.
Any form of bleeding occurring in the eye. Since there are signals for retinal vessel occlusions, this one is probably related to them.
A review of ocular adverse events associated with COVID vaccination
A type of migraine that involves the vestibular organ and can occur with or without headaches, causing dizziness, motion sickness and loss of balance.
An article on vestibular adverse events associated with COVID vaccination
Tinnitus is a variety of sound that is heard when no corresponding external sound is present.
A hypertensive emergency is an acute, marked elevation in blood pressure that is associated with signs of target-organ damage. These can include pulmonary edema, cardiac ischemia, neurological deficits, acute renal failure, aortic dissection, and eclampsia. The incidence after COVID vaccination is estimated to be 0.6%
This article proposes pathomechanisms of post-vaccination hypertensive emergencies
A superficial thrombophlebis is an inflammation of one of the veins located underneith your skin. In most cases this happens due to blood clots being present in the affected vein.
It seems there are no scientific articles describing the occurrence of thrombophlebitides after COVID vaccination, possibly because it is usually a benign, albeit potentially long and painful process.
Internal bleeding or internal hemorrhage is a loss of blood from a vessel inside the body. The blood is usually not visible from outside of the body. It is caused by traumatic or non-traumatic rupturing of blood vessels, medication, thrombocytopenia and other disorders.
An article on immune thrombocytpenia after modRNA vaccination
Blood clots originating in the lung and presenting similarly to pulmonary embolisms. It has been proposed that these are a manifestation of local inflammation. Happens in COVID. Happens after vaccination
Pulmonary embolisms are clots arising from other parts of the body - usually the legs where blood flow is slower - before becoming stuck in an arterial vessel inside the lung, blocking that vessel and causing anything from no symptoms at all over shortness breath, rapid breathing and coughing blood to sudden death, depending almost solely on the size of the clot.
Unfortunately there is very little to be found in scientific literature about thrombotic events and hypercoagulability after modRNA vaccination. This is a case series.
There are superficial and deep veins. Superficial veins run under the skin, outside of the body fascia, while deep veins run inside the body fascia. As the name suggests, a deep vein thrombosis is a clot that forms inside the deep veins, most commonly in the legs where the blood flow is slower.
Again, all I can offer is this case series.
Any blood clot forming inside a blood vessel, arterial or venous.
Bell’s palsy is a malfunction of the facial nerve, which is the seventh cranial nerve.
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves, which are nerves emerging directly from the brain, innervating tissue in the head and torso.
Cranial nerve VII controls the facial muscles, supplies taste fibers and provides parasympathic innervation to a number of glands.Bells’s palsy is characterized by a one-sided facial droop - better known as the “Pfizer Smile”.
The 4th cranial nerve is the trochlear nerve which only function is to move the eye, abducting it, depressing it and rotating it inwards. Like any other nerve, it can become paralyzed, resulting in loss of control over eye movement.
Bell’s palsy can come with taste disorder, but only in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue (the outer 2/3) - other taste disorders are probably caused by spike-mediated effects.
The glossopharyngeal nerve is the 9th cranial nerve and the one that supplies sensory fibers to the pharynx among many functions. Paresthesiae are abnormal sensations - usually superficial - like tingling, burning or numbness.
There’s no publication on this, but here is one on hypoglossal nerve palsy - the 12th cranial nerve. Starting to see a pattern, yet?
Anosmia is loss of smell. The olfactory nerve is the 1st cranial nerve.
Seeing all these cranial nerve dysfunctions, could mental fatigue be immune-mediated?
Chil(l)blains aka pernio or “COVID toes” describes inflammation of the capillaries in the hands and feet, particularly upon exposure to cold or humidity. It is not just a symptom of Chilblain Lupus erythematodes (CHBL1), but also of COVID disease and vaccination.
I suppose that’s just what happens when these peripheral capillaries express viral protein.
The term edema describes water accumulating where it shouldn’t. Pulmonary edema occurs in the lungs and is a life-threatening condition, beacause it limits gas exchange.
The signal could be related to pulmonary embolisms which increase the pressure in pulmonary arteries that transport blood from the heart to the lung.
It could also have a cardiac cause. When the left ventricle of the heart fails, blood accumulates in the vessels behind it which are carrying oxygenated blood from the lung to the heart. This increases the pressure in those veins and leads to water accumulating in the lung.
Or it could be pneumonitis. Further analysis of co-occurrences could answer these questions.
Ischemia is a lack of oxygen due to reduced blood flow. The liver can be affected due to shock, but considering these patients took modRNA vaccines, blood clots in the hepatic artery being causal here is certainly not that unlikely.
There is a report of hepatic artery occlusion after AstraZeneca vaccination
Inflammation of the appendix, a dead end in the first section of your colon.
I found no sign of this in German hospital data.The association between COVID vaccines has been investigated numerous times, despite VAERS signal being much weaker than for thrombotic events (limited hangout?), possibly because there were calls for investigation, but no increased incidence was found.
Diverticulitis
Inflammation in acquired pouches of the colon, so-called diverticles. Diverticulitis can cause rupture of the colon, most often resulting in death, just like appendicitis can result in death, if left untreated.
Here is an article about the various gastrointestinal issues reported to VAERS
Embolic stroke occurs when a clot migrates (this is called an embolism) from its source to block a cerebral artery, resulting in lack of perfusion to part of the brain and ultimately cell death. The clots usually originate from the heart or arterial vessels leading from the heart to the brain, but they can occasionally originate from venous vessels as well, if there is a shunt in the heart, allowing the clot to travel from right to left side of the heart.
Cerebral artery occlusion / Cerebral artery stenosis
The cerebrum is the large walnut-like looking part making up around 80% of your brain mass. About 45% of strokes occur inside this region. The artery most frequently involved is the middle cerebral artery. When it becomes clogged this will usually present with signs most commonly associated with stroke, like hemiparesis and sensory loss.
The cerebellum is a small part of the brain located in the back, underneith the walnut-like structure that is the cerebrum. It is important for motorcoordination. Depending on which of the three large arteries is affected, cerebellar strokes can present with and without ataxia (loss of motorfunction). Other possible symptoms are headaches, nausea, nystagmus, but also sensory loss of pain and temperature.
Basal ganglia are a group of nerve cell clusters inside the brain that are responsible for a large array of learning, cognitive, emotional and motorical functions. Haemorrhagic strokes are the most common form of stroke in basal ganglia, are often a result of high blood pressure and presents with cognitive, sensory and motorical dysfunction, as well as headaches.
Case report of basal ganglia haemorrhage after modRNA vaccination
Lacunes are empty spaces in various deep regions of the brain, that arise when penetrating arteries supplying the respective region with blood become obstructed. While sometimes silent, when lacunar infarctions do present with symptoms these are usually motorical and sensory loss of function.
The thalamus is a very small region in the center of the brain, which relays motor and sensory signals and also plays an important role in alertness, mood, speech and pain processing. Infarctions usually present with impaired sensory function, that can transition into a debilitating pain syndrome called Dejerine–Roussy syndrome.
A case report of a modRNA-vaccinated patient suffering bilateral (both sides) thalamic stroke
Cerebral small vessel ischaemic disease
CVSD (Cerebral Small Vessel Disease) describes a process in which the smallest of vessels in the cerebrum become clogged, that is very common among elders, contributing to about 20% of strokes and 45% of dementias.
Ischaemic strokes are caused by clots blocking the blood flow to parts of the brain.
Haemorrhagic strokes are caused by ruptured blood vessels in the brain.
Cerebrovascular accident is a general term describing all of the above concepts. An interruption of blood flow to parts of the brain.
Population-level Data
The signals that should be reflected in mortality figures can be grouped into three categories:
Strokes (ICD-10 codes I60-I69)
Myocardial infarctions (ICD-10 codes I21.0-I21.9)
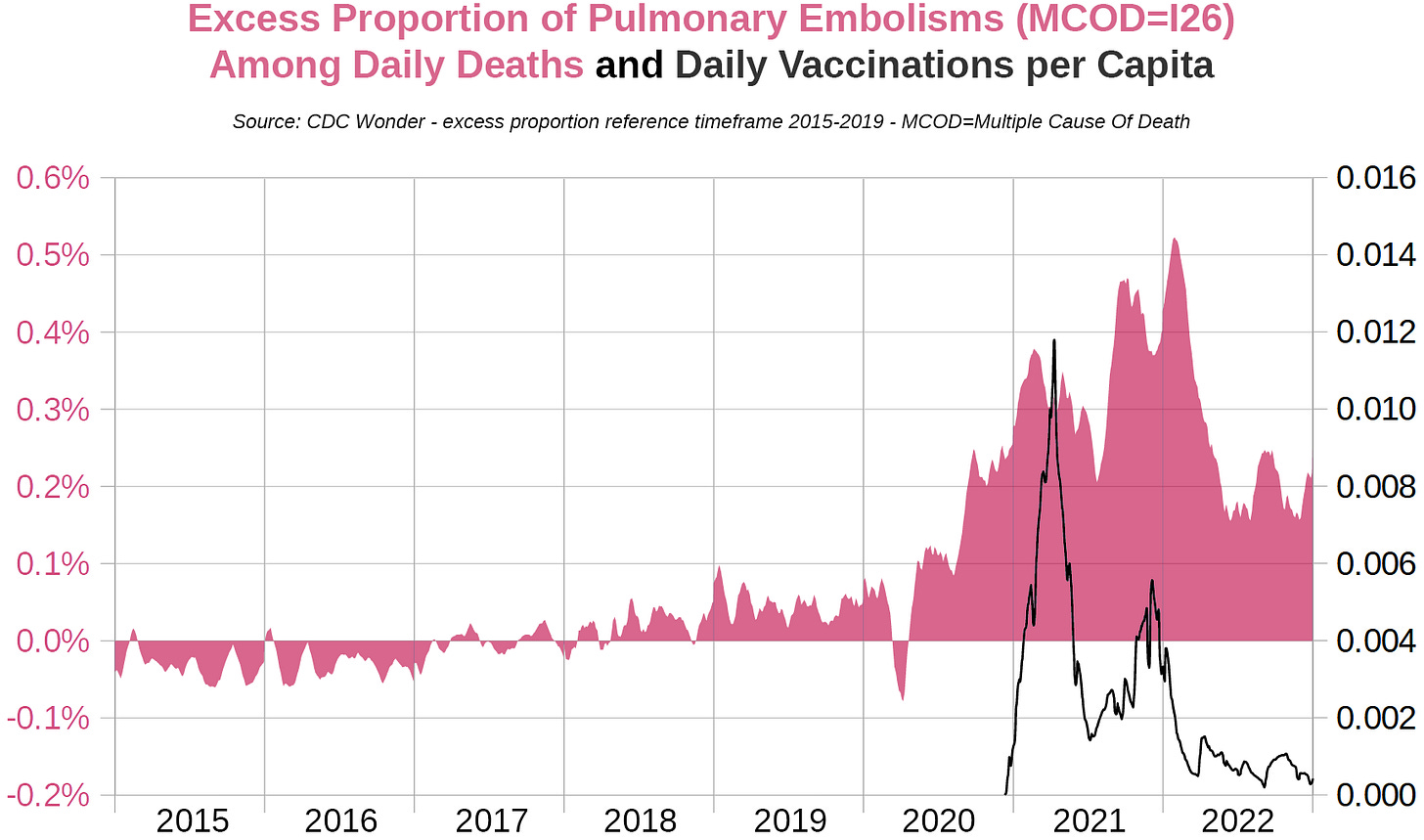
Lung embolisms (ICD-10 code I26.0-I26.9)
We are going to have a look at all three next to the number of administered vaccine doses per capita.
I will express the number of deaths where the respective diagnostic codes were mentioned anywhere on the death certificate as proportions among…
all deaths
non-COVID deaths
From these timeseries I am calculating an excess series with 2015-2019 as reference timeframe to remove seasonal influences.
Strokes
Due to the high number of COVID-associated deaths the proportion of cerebrovascular deaths saw a deficit of 0.7% in late 2020. Between onset and peak of the initial vaccination campaign this deficit turned into an excess of 0.3%. However, COVID mortality rates fell simultaneously, so we should expect the proportion of cerebrovascular deaths among all deaths to increase during this time.
Something similar happens during the booster campaign in the 4th quarter, but this was also accompanied by declining COVID mortality, so we are going to look at the proportion among non-COVID deaths next.
The proportion among non-COVID deaths started increasing shortly before the vaccination campaign commenced in December 2020 and peaks in early 2021. As soon as vaccination rates decline, so does the proportion of cerebrovascular deaths among non-COVID deaths.
The booster campaign seems to coincide with another increase, followed by a large excess throughout 2022. There was just so much going on at the time that it is hard to pin this on vaccines based on these observations alone.
However, considering the large number of cerebrovascular safety signals and the fact that the proportion of cerebrovascular deaths among non-COVID deaths is much higher in 2021 and 2022 compared to 2020, a causal link seems plausible.
Myocardial infarctions
The two largest vaccination rate peaks clearly correspond to peaks in the proportion of acute myocardial infarctions among deaths, but as I have mentioned before, COVID deaths were in decline, so the proportion is expected to increase. In mid-2021 there is another peak that does not correspond with vaccinations
We will now look at the proportion of decedents with heart attacks among non-COVID deaths.
The timeseries is corrected for the apparent linear downward trend between 2015-2019 that you saw in the previous chart. In 2020, this downward trend was clearly broken, which is to be expected when people have their “pants scared off”.
The situation relaxed a little in the course of 2020, but as soon as vaccinations commenced in December, the proportion of acute myocardial infarctions among non-COVID deaths shot up and remained elevated throughout 2021, when the largest share of vaccine doses was administered.
These upward deviations from the downward trend we are seeing throughout 2021 are more suggestive of a short-term effect on cardiac mortality, while cerebrovascular mortality continued to be elevated well into 2022.
Pulmonary embolisms
Despite the enormous increase in mortality that the USA saw in 2020, the proportion decedents with lung embolisms shot up after the initial “COVID wave” that began in March. A week or two after the start of the vaccination campaign the proportion increased steeply until February, then declines until mid-2021, before rising again along with the number of administered vaccine doses.
Proportions of embolisms among non-COVID deaths rise steepy with the onset of the vaccination campaign and peak shortly before vaccination rates peak. While proportions are highest in 2021, there is something happening in 2022 as well, which is not well-explained by acute vaccination effects.
Conclusion
There are four important signal clusters emerging from spontaneous reports:
Cardiac signals made up of arrythmias and concepts surrounding heart attacks
Cerebrovascular signals, both haemorrhagic and ischemic
With 4 affected nerves, non-vascular neurological signals are almost exclusively related to cranial nerve dysfunction
Reproductive system disorders centered around menstruation
Population-level data shows that proportions of decedents who had diagnoses for cerebrovascular disease, acute myocardial infarction or lung embolisms were either peaking in 2021 and 2022 or - in the case of acute myocardial infarction - diverging upwards from the previous downward trend.
While cardiac signals have been well-described in scientific literature, this is not the case for neuroinflammatory disorders. Cranial nerve dysfunction has received little attention from the scientific community.
















Thank You Fabian for this needed information!
Thank you! Wonderful resource you provided here!